Example 1: Continuity
The function f(x) = x^2 is continuous at x = 2 because the limit of f(x) as x approaches 2 from either side is 4, which is the same as the value of f(2).
Example 2: Discontinuity
The function g(x) = 1/x is discontinuous at x=0 because the limit of g(x) as x approaches 0 from either side is not defined.
In summary, continuity and limit are important concepts in calculus that allow us to understand the behavior of functions at specific points. A function is continuous at a point if it has a well-defined value and that value is the same regardless of the direction from which it is approached. Discontinuity occurs when a function does not have a value at a particular point or when the value of the function changes abruptly as the input approaches a particular value.If you are looking for Limits and Continuity | Calculus | Pinterest you've came to the right web. We have 6 Pictures about Limits and Continuity | Calculus | Pinterest like Limits and Continuity - YouTube, continuity of limits - YouTube and also 1.4. Limits and Continuity - Example1 - Part1 - YouTube. Read more:
Limits And Continuity | Calculus | Pinterest
calculus math continuity limits ap classroom teacher limit mathematics teaching curious maths function education choose board
Limits And Continuity - YouTube
 www.youtube.com
www.youtube.com continuity limits
1.4. Limits And Continuity - Example1 - Part1 - YouTube
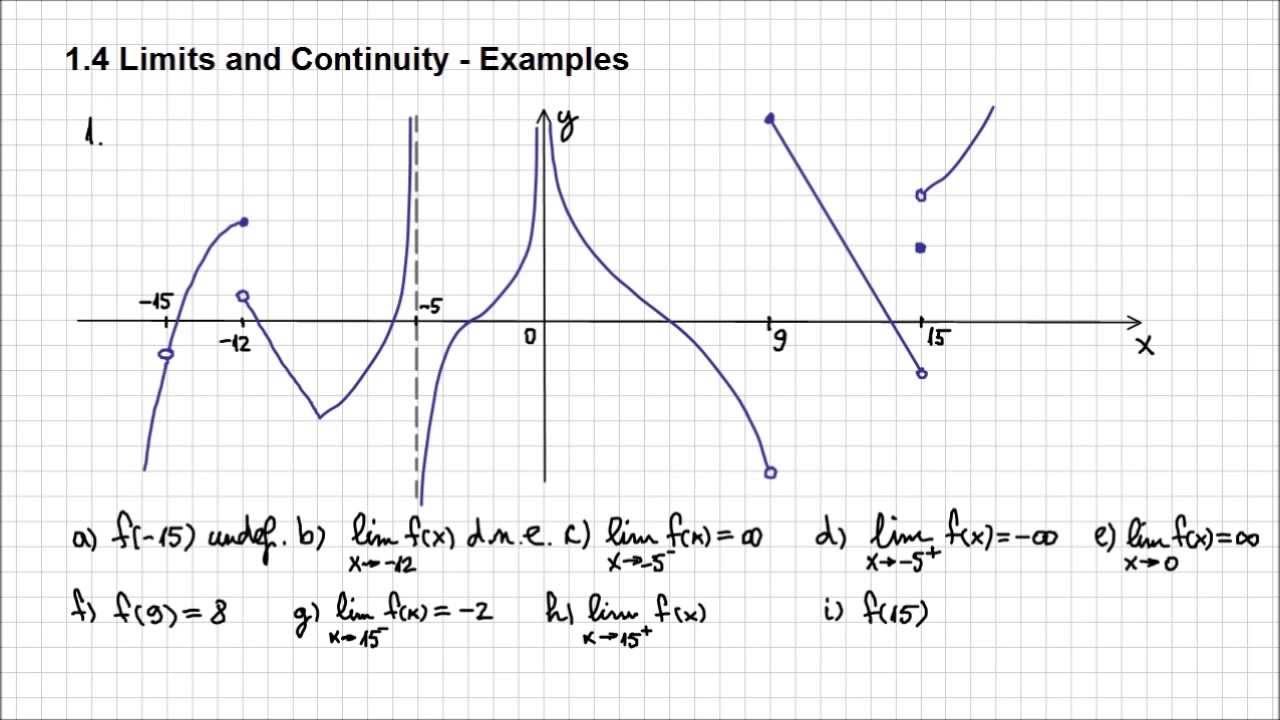 www.youtube.com
www.youtube.com continuity limits
11X1 T08 01 Limits & Continuity
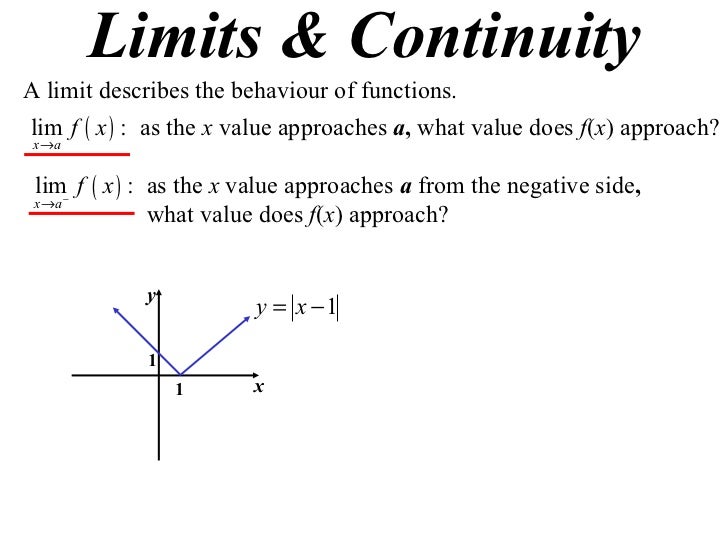 www.slideshare.net
www.slideshare.net continuity t08 11x1
Continuity Of Limits - YouTube
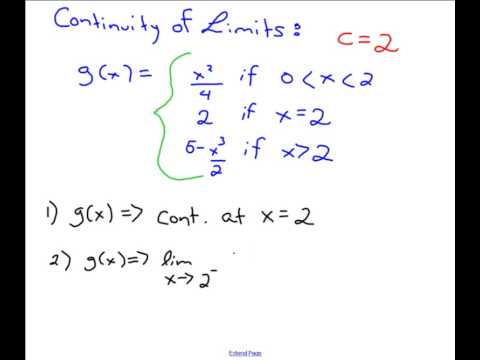 www.youtube.com
www.youtube.com continuity limits
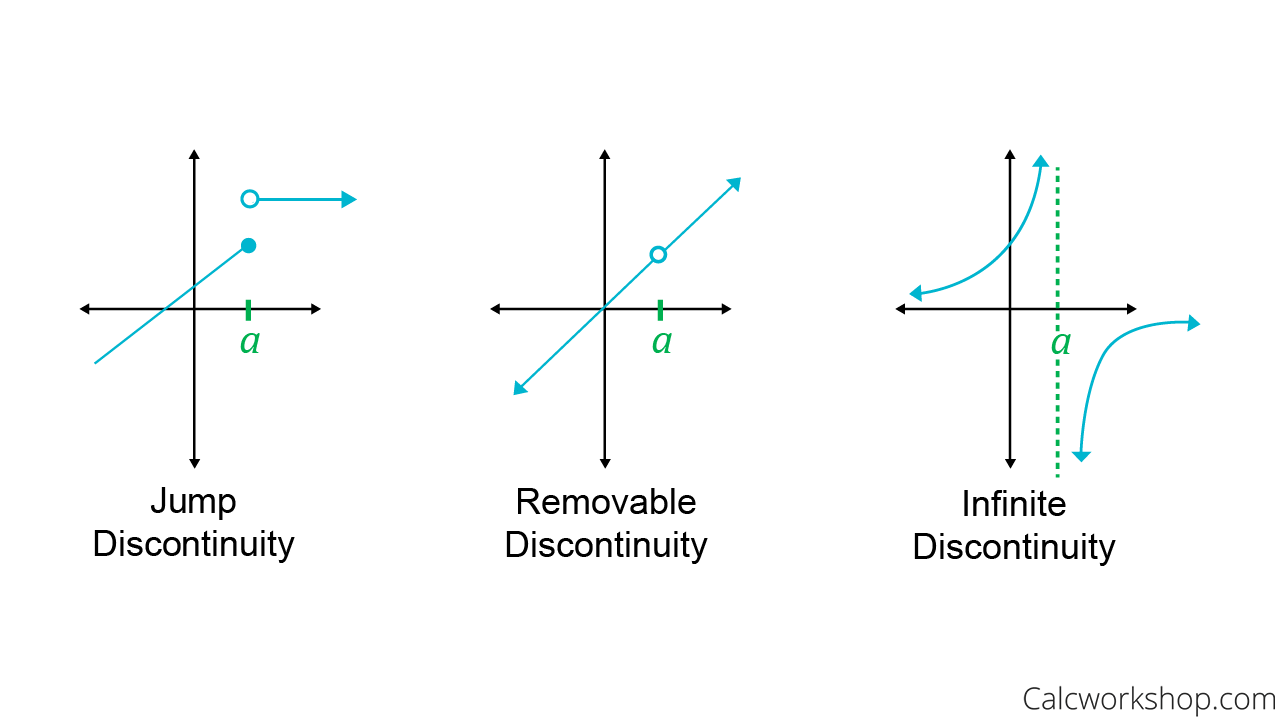
Limits And Continuity - 2 Sure Fire Examples!
 calcworkshop.com
calcworkshop.com continuity discontinuity limits types continuous discontinuous graphs examples functions calcworkshop illustrations
Continuity t08 11x1. Continuity discontinuity limits types continuous discontinuous graphs examples functions calcworkshop illustrations. Continuity limits

No comments:
Post a Comment